La fin de l’assistance windows 10 est le 14 oct. 2025. Êtes-vous prêt?
Microsoft mettra fin à l’assistance pour Windows 10 le 14 octobre 2025, ce qui signifie qu’il n’y aura plus d’assistance technique, de correctifs de sécurité, ni de mises à jour automatiques de Windows. Votre organisation est-elle prête ? Portez le Évaluation de la préparation en fin de soutien de Windows 10 dès aujourd'hui.
Disaster Recovery Planning for IT: Comprehensive Guide
Disaster recovery planning is a critical component of IT infrastructure management. It ensures that organizations can quickly recover and resume operations after unexpected disruptions, such as natural disasters, cyberattacks, hardware failures, or human errors. A well-designed disaster recovery plan minimizes downtime, protects sensitive data, and maintains business continuity. This guide will explore the key components, strategies, and best practices for creating an effective disaster recovery plan tailored to IT environments.
Key Workloads to Protect in Disaster Recovery Planning
Critical Business Applications
Why Protect Them: Business applications are the backbone of operations, enabling organizations to manage customer relationships, process transactions, and execute workflows. Downtime in these applications can lead to financial losses, customer dissatisfaction, and reputational damage.
How to Protect Them: Implement regular backups, redundancy measures, and failover systems to ensure these applications remain operational during disruptions. Prioritize applications based on their impact on business continuity.
Databases and Data Warehouses
Why Protect Them: Databases store vital information, including customer data, financial records, and operational metrics. Losing or corrupting this data can result in compliance violations, operational inefficiencies, and loss of trust.
How to Protect Them: Use automated backup solutions, replication across multiple sites, and encryption to safeguard data integrity. Regularly test recovery procedures to ensure data can be restored quickly.
Virtual Machines and Cloud Workloads
Why Protect Them: Virtual machines and cloud workloads are increasingly used for scalability and flexibility. However, they are vulnerable to outages, misconfigurations, and cyber threats.
How to Protect Them: Leverage cloud-native disaster recovery tools, snapshot technologies, and multi-region deployments to ensure resilience. Monitor workloads for anomalies and implement security measures to prevent breaches.
Network Infrastructure
Why Protect Them: Network infrastructure, including routers, switches, and firewalls, is essential for connectivity and communication. A failure in the network can disrupt access to critical systems and services.
How to Protect Them: Maintain redundant network paths, implement failover protocols, and regularly update firmware to prevent vulnerabilities. Document network configurations for faster recovery.
End-User Devices
Why Protect Them: End-user devices, such as laptops and desktops, are often overlooked in disaster recovery planning. However, they store important files and provide access to business systems.
How to Protect Them: Use endpoint backup solutions, remote wipe capabilities, and device management tools to protect data and ensure quick recovery. Train employees on best practices for data security.
Steps to Create a Disaster Recovery Plan
Step 1: Assess Risks and Threats
Begin by identifying potential risks and threats to your IT environment. These may include natural disasters, cyberattacks, hardware failures, software bugs, and human errors. Conduct a thorough risk assessment to understand the likelihood and impact of each threat.
Step 2: Define Recovery Objectives
Set clear recovery objectives, including Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO). RTO specifies the maximum acceptable downtime, while RPO defines the maximum acceptable data loss. These objectives will guide the design of your disaster recovery plan.
Step 3: Inventory IT Assets
Create a detailed inventory of all IT assets, including servers, applications, databases, network devices, and end-user devices. Categorize assets based on their criticality to business operations.
Step 4: Design Redundancy and Backup Solutions
Implement redundancy measures, such as failover systems and load balancing, to ensure high availability. Establish backup solutions, including automated backups, offsite storage, and cloud-based replication, to protect data and systems.
Step 5: Develop a Communication Plan
During a disaster, clear communication is essential. Develop a communication plan that outlines roles, responsibilities, and contact information for key stakeholders. Include protocols for notifying employees, customers, and partners.
Step 6: Test and Validate the Plan
Regularly test your disaster recovery plan to identify gaps and ensure its effectiveness. Conduct simulated disaster scenarios to validate recovery procedures and train employees on their roles.
Step 7: Update the Plan Continuously
Disaster recovery planning is not a one-time effort. Continuously update the plan to reflect changes in your IT environment, emerging threats, and lessons learned from testing.
Best Practices for Disaster Recovery Planning
Prioritize Critical Systems
Focus on protecting systems that are essential to business continuity. Use risk assessments to identify and prioritize these systems.
Automate Backup Processes
Manual backups are prone to errors and inconsistencies. Automate backup processes to ensure data is consistently protected and easily recoverable.
Leverage Cloud Solutions
Cloud-based disaster recovery solutions offer scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. Use cloud services for data replication, failover, and storage.
Implement Multi-Layer Security
Protect your IT environment with multi-layer security measures, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption. Regularly update security protocols to address emerging threats.
Train Employees
Employees play a crucial role in disaster recovery. Provide training on data security, recovery procedures, and communication protocols to ensure they are prepared for disruptions.
Strengths and Drawbacks of Disaster Recovery Planning
Strengths
Minimized Downtime: A well-designed disaster recovery plan reduces downtime, enabling organizations to resume operations quickly after disruptions.
Data Protection: Regular backups and redundancy measures safeguard sensitive data from loss or corruption.
Business Continuity: Disaster recovery planning ensures that critical systems remain operational, maintaining customer trust and operational efficiency.
Compliance: Many industries have regulatory requirements for data protection and disaster recovery. A robust plan helps organizations meet these requirements.
Cost Savings: While disaster recovery planning requires upfront investment, it prevents costly downtime and data loss, saving money in the long run.
Drawbacks
Initial Costs: Implementing disaster recovery solutions, such as backup systems and failover infrastructure, can be expensive.
Complexity: Designing and maintaining a disaster recovery plan requires expertise and ongoing effort, which can be challenging for smaller organizations.
Testing Challenges: Regular testing is essential but can be disruptive to operations. Organizations must balance testing with minimizing impact on daily activities.
Human Error: Despite planning, human error can still occur during recovery procedures, leading to delays or mistakes.
Evolving Threats: As technology evolves, new threats emerge. Organizations must continuously update their disaster recovery plans to address these threats.
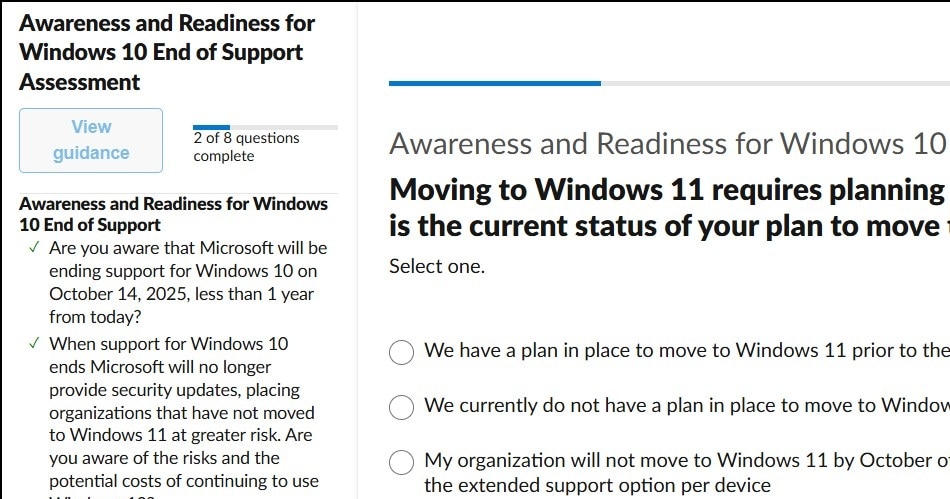
Y a-t-il un outil pour m’aider à tester par la compatibilité de Windows 10 EOS (fin de l’assistance) ?
Oui, vous pouvez utiliser le Sensibilisation et préparation pour Windows 10 Fin de l’assistance outil d’évaluation. [Si votre navigateur ne vous mène pas directement à l’outil, faites défiler la page jusqu’à son emplacement au bas de la page.] Il s’agit d’un questionnaire simple, simplement de questions à choix multiples, pour tester votre préparation et celle de votre entreprise à passer de Windows 10 à Windows 11. Après avoir terminé, vous obtiendrez une évaluation des risques et des conseils sur les prochaines étapes.
Qu’est-ce que la planification de restauration en cas de désastre dans les TI ?
Disaster recovery planning in IT involves creating strategies and procedures to recover and resume operations after disruptions, such as cyberattacks, hardware failures, or natural disasters. It focuses on minimizing downtime, protecting data, and maintaining business continuity.
Why is disaster recovery planning important?
Disaster recovery planning is important because it ensures business continuity, protects sensitive data, and minimizes financial losses during disruptions. It also helps organizations meet regulatory requirements and maintain customer trust.
What are RTO and RPO in disaster recovery?
Recovery Time Objective (RTO) is the maximum acceptable downtime, while Recovery Point Objective (RPO) is the maximum acceptable data loss. These metrics guide the design of disaster recovery plans.
How do I assess risks for disaster recovery planning?
Assess risks by identifying potential threats, such as natural disasters, cyberattacks, hardware failures, and human errors. Evaluate the likelihood and impact of each threat to prioritize mitigation efforts.
What are the key components of a disaster recovery plan?
Key components include risk assessment, recovery objectives, IT asset inventory, redundancy measures, backup solutions, communication plans, and testing procedures.
How often should I test my disaster recovery plan?
Test your disaster recovery plan at least annually or whenever significant changes occur in your IT environment. Regular testing ensures the plan remains effective and identifies gaps.
What are the benefits of cloud-based disaster recovery?
Cloud-based disaster recovery offers scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. It enables data replication, failover, and storage across multiple regions, enhancing resilience.
How can I protect critical business applications?
Protect critical business applications by implementing regular backups, redundancy measures, and failover systems. Prioritize applications based on their impact on business continuity.
What is the role of employees in disaster recovery?
Employees play a crucial role in disaster recovery by following recovery procedures, maintaining data security, and communicating effectively during disruptions. Training is essential to prepare them for these responsibilities.
How do I create a communication plan for disaster recovery?
Create a communication plan by outlining roles, responsibilities, and contact information for key stakeholders. Include protocols for notifying employees, customers, and partners during disasters.
What are the challenges of disaster recovery planning?
Challenges include initial costs, complexity, testing disruptions, human error, and evolving threats. Organizations must address these challenges to ensure effective disaster recovery.
How can I minimize downtime during recovery?
Minimize downtime by implementing failover systems, automating recovery procedures, and prioritizing critical systems. Regular testing ensures recovery processes are efficient.
What is the difference between backup and disaster recovery?
Backup involves creating copies of data for protection, while disaster recovery focuses on restoring systems and operations after disruptions. Both are essential for business continuity.
How do I choose the right disaster recovery solutions?
Choose solutions based on your organization's needs, budget, and IT environment. Consider factors such as scalability, ease of use, and compatibility with existing systems.
What are the risks of not having a disaster recovery plan?
Risks include prolonged downtime, data loss, financial losses, compliance violations, and reputational damage. A lack of planning leaves organizations vulnerable to disruptions.
How can I ensure data integrity during recovery?
Ensure data integrity by using automated backup solutions, encryption, and replication across multiple sites. Regularly test recovery procedures to verify data accuracy.
What is the role of redundancy in disaster recovery?
Redundancy ensures high availability by providing backup systems and failover infrastructure. It minimizes the impact of hardware failures and other disruptions.
How do I update my disaster recovery plan?
Update your plan continuously to reflect changes in your IT environment, emerging threats, and lessons learned from testing. Regular reviews ensure the plan remains effective.
What industries require disaster recovery planning?
Industries such as finance, healthcare, retail, and manufacturing require disaster recovery planning due to regulatory requirements and the need for business continuity.
Can small businesses implement disaster recovery plans?
Yes, small businesses can implement disaster recovery plans by leveraging cost-effective solutions, such as cloud-based backups and automated processes. Planning is essential for protecting operations and data.
Disaster recovery planning is a vital aspect of IT management, ensuring organizations can recover and resume operations after disruptions. By identifying risks, defining recovery objectives, and implementing redundancy measures, businesses can protect critical systems and maintain continuity. Regular testing, employee training, and continuous updates are essential for effective disaster recovery planning.